 |
| (2) Symptoms of periodontitis |
This disease is interestingly initiated when the bacteria in our mouths, along with mucus and other substances, create "plaque" on our teeth. This plaque that is not removed can become hard and create "tarter" that cannot be cleaned by yourself. The longer these two substances are in our teeth can cause inflammation of the gums. The immune system fights this bacteria as plaque is spread throughout our mouth, especially at the gum line. The immune system also starts to break down bone and connective tissue that hold the teeth intact. When this is not treated by a professional, the bones, gums, and tissue that hold the teeth break down and cause the tooth to be permanently removed.
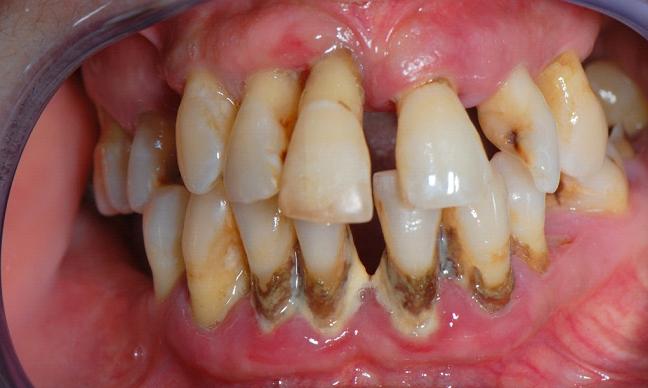 |
| (3) Patient with periodontitis |
References:
(1) http://www.nidcr.nih.gov/oralhealth/Topics/GumDiseases/PeriodontalGumDisease.htm#intro
(2) http://periodontalhealth.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/06/gum-visual-6.jpg
(3) http://www.natural-health-news.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/02/Periodontitis.jpg




